

Decision analysis model buildingThe following DRM represents the classical decision analysis cycle model refinement following the reiterative evaluation of deterministic, probabilistic and informational phases following R. Howard, Decision Analysis Approach, SRI & Stanford University, 1968-2015) 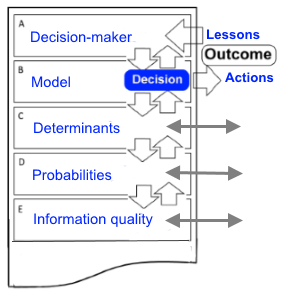 |
|
|
This section is being updated with a range of recent applications for DRMs including:
- over 300 policy annual report analytical calculations for an annual agicultural report
- over 80 analytical tools for project design to comply with Agenda 2030 Sustainable Development Goal objectives
|
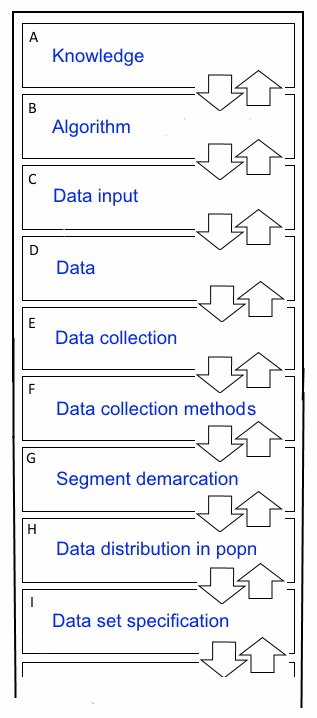
Data Reference Models can be used for a wide range of applications. Below there are three representations for:
- a general schemata of functions that would normally be placed into a DRM
- a process model such as a manufacturing process
- a policy model that requires specific information
|

Experimental and survey design needs to take into account the physical distribution of the objects whose properties need to be measured to generate the appropriate dataset to acquire the desired knowledge on specific relationships. In the case of river basins and analysis of water flux, the existing catchment area is normally divided into segments distributed down the complete run of the river within which stratified data is to be collected.
General logic for river basin data
 |
|
|
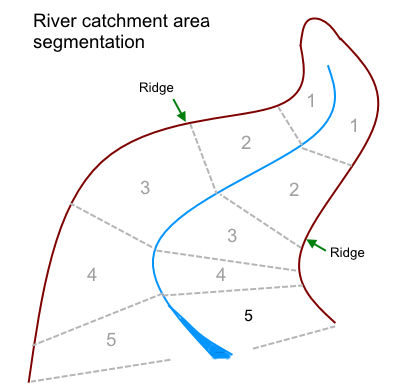
For each specific aspect of knowledge, if there is a requirement for a different dataset and associated algorithms, it is advisable to create a separate DRM to each output requirement. This helps maintain transparency on the total dataset requirement which is made up of the sum of DRM datasets after deducting duplicate data. In natural resource systems there is normally a variance in data according to the geographic locational and altitude and timing of data collection within a day or over the year. In data collection, periodic frequency can have important implications for the utility of the data in the knowledge generation models for which it is intended.

More advanced DRMs involve a range of considerations linked to due diligence procedures and analytical methologies. With climate change andthe combination of rising temperatures and loss of water from environments where temperatures are rising the locational-states of critical variables (LST-Locational-State Theory considerations) become of increasing significance in understanding the primary data elements to be collected. This has an important contribution to statistical design of data collection configurations and methods.

For example LST has a fundamental tole in specifying appropriate population stratifications based on, for example, farm typologies used to lower survey sample size and to raise data precision in terms of population segement representation accuracy (low variance).

Accumulogs are immutable database sections that introduce an important tactical security advantage to statistical records of increasing importance under climate change. Because they are imutable they are not subject to alteration. Any changes are added separately with explanations for any change. Accumulogs have exactly the same function as blockchain which appeared in the 2000s associated with crypto-currencies.
Both Locational State Theory and Accumulogs were identified in 1985 by Hector McNeill as being essential elements in learing systems. Most current advanced in these fields are coordinated by SEEL-Systems Engineering Economics Lab.
